Wireless Electricity: Powering the Future
In a world where technology is constantly advancing, the concept of wireless electricity is no longer just a figment of science fiction. It is now a reality that has the potential to revolutionize the way we power our devices and ultimately change the future of energy consumption.
The Rise of Wireless Power Transmission
Wireless power transmission, also known as wireless electricity, is the transmission of electrical energy from a power source to an electrical load without the need for physical connections such as wires or cables. This technology has been in development for decades, with early experiments dating back to the late 19th century. However, recent advancements in technology have brought wireless electricity closer to becoming a mainstream reality.
How Does Wireless Electricity Work?
The basic principle behind wireless electricity is electromagnetic induction. This process involves the transfer of energy between two coils through a magnetic field. When an electric current flows through the primary coil, it creates a magnetic field that induces a current in the secondary coil, thus transferring power wirelessly.
Advantages of Wireless Electricity
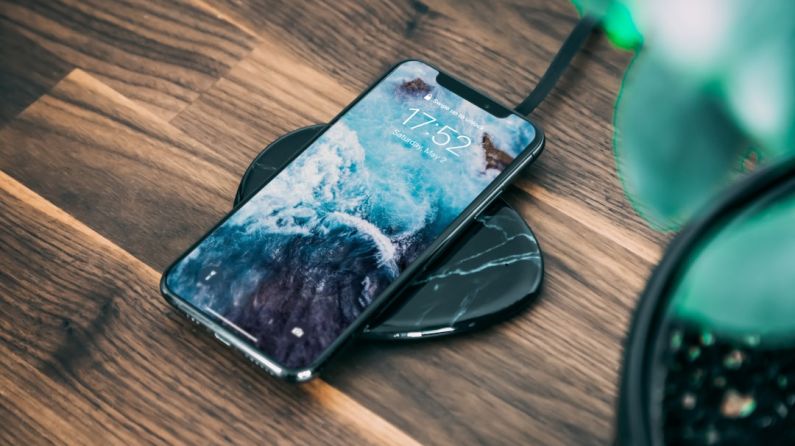
One of the key advantages of wireless electricity is convenience. Imagine a world where you no longer have to plug in your devices to charge them. With wireless charging pads or stations, you can simply place your device on a surface and have it charge automatically. This not only eliminates the need for tangled cords but also makes charging more accessible and user-friendly.
Another significant advantage of wireless electricity is its potential impact on the environment. By reducing the reliance on traditional power cords and cables, wireless power transmission can help minimize electronic waste and promote sustainability. Additionally, the efficiency of wireless charging systems can lead to energy savings in the long run.
Applications of Wireless Electricity
The applications of wireless electricity are vast and varied, ranging from consumer electronics to industrial systems. In the consumer sector, wireless charging technology is already integrated into smartphones, smartwatches, and other portable devices. As this technology advances, we can expect to see wireless charging become more widespread in public spaces, homes, and vehicles.
In the healthcare industry, wireless electricity has the potential to revolutionize medical devices and equipment. Wireless power transmission can enable implantable medical devices to be charged wirelessly, eliminating the need for invasive procedures to replace batteries. This technology could also be used in hospitals to power medical equipment without the risk of electrical hazards.
Challenges and Limitations
While the potential of wireless electricity is promising, there are still challenges and limitations that need to be addressed. One of the main challenges is the efficiency of wireless power transmission. Current systems have lower efficiency levels compared to traditional wired connections, leading to energy loss during the transfer process.
Another challenge is the range of wireless power transmission. Most wireless charging systems have a limited range, requiring devices to be in close proximity to the charging source. As technology advances, researchers are working on developing long-range wireless power transmission systems that can transmit power over greater distances.
The Future of Wireless Electricity
As technology continues to evolve, the future of wireless electricity looks bright. With ongoing research and development in the field, we can expect to see advancements in efficiency, range, and scalability of wireless power transmission systems. This technology has the potential to transform the way we interact with energy and pave the way for a more sustainable and connected future. Wireless electricity is not just a concept anymore—it is a tangible reality that has the power to shape the future of power consumption and distribution.