Biometric Security: the End of Passwords?
In a world where data breaches and cyber-attacks are becoming increasingly common, the traditional password may no longer suffice as a reliable form of security. As technology advances, the use of biometric authentication methods is gaining momentum as a more secure and convenient alternative. Biometric security, which uses physical and behavioral characteristics to verify a person’s identity, offers a promising solution to the vulnerabilities associated with passwords. Could biometric security be the end of passwords as we know them?
The Rise of Biometric Security
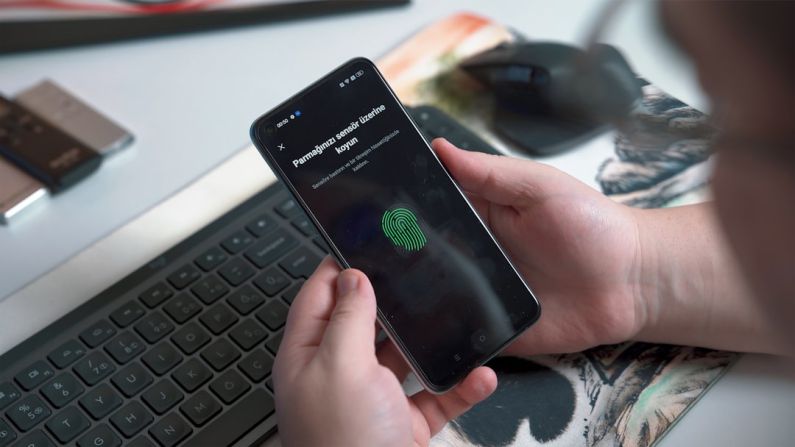
Biometric security has been on the rise in recent years, with many devices and systems now incorporating biometric features for authentication. From fingerprint scanners on smartphones to facial recognition technology at airports, biometric security is becoming more prevalent in our daily lives. Unlike passwords, which can be easily forgotten, stolen, or hacked, biometric data is unique to each individual, making it much more difficult to replicate or falsify.
Enhanced Security and Convenience
One of the key advantages of biometric security is its enhanced level of security compared to traditional passwords. Biometric identifiers, such as fingerprints, iris patterns, and facial features, are difficult to duplicate, making them highly secure forms of authentication. In addition, biometric authentication eliminates the need for users to remember complex passwords or worry about their credentials being compromised.
Moreover, biometric security offers greater convenience for users. With biometric authentication, users can simply use their fingerprint, face, or voice to access their devices or accounts, eliminating the need to type in passwords repeatedly. This not only saves time but also enhances the user experience by providing a seamless and efficient authentication process.
Challenges and Concerns
While biometric security offers numerous benefits, it is not without its challenges and concerns. One of the main concerns surrounding biometric authentication is the issue of privacy and data protection. Biometric data, being highly sensitive and personal, raises questions about how this information is stored, used, and protected from unauthorized access.
Another challenge is the risk of biometric data being compromised. Unlike passwords that can be changed if they are stolen, biometric data, such as fingerprints or facial features, cannot be reset. If biometric data is breached, individuals may face serious consequences, as this information is irreplaceable and permanent.
The Future of Biometric Security
Despite the challenges, the future of biometric security looks promising. As technology continues to evolve, biometric authentication methods are expected to become even more sophisticated and secure. Advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning are enabling biometric systems to accurately authenticate individuals in real-time, making them more reliable and efficient.
Moreover, the integration of biometric security into various devices and systems is expected to continue expanding. From smartphones and laptops to bank ATMs and smart home systems, biometric authentication is becoming increasingly integrated into everyday technologies, making it more accessible to a wider audience.
Conclusion: A New Era of Security
As biometric security continues to gain traction, the days of relying solely on passwords for authentication may be numbered. The unique advantages of biometric authentication, including enhanced security and convenience, make it a compelling alternative to traditional password-based systems. While challenges remain, ongoing advancements in biometric technology are paving the way for a new era of security that prioritizes both protection and user experience. With biometric security on the rise, could this be the end of passwords as we know them? Only time will tell.