Ai and Wildlife Conservation: a New Hope
In recent years, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) technology in various sectors has been nothing short of revolutionary. From healthcare to finance, AI has proven its potential to transform industries and streamline processes. One area where AI is making a significant impact is wildlife conservation. With the increasing threat to biodiversity and ecosystems around the world, AI offers new hope for protecting and preserving our planet’s precious wildlife.
AI in Monitoring and Surveillance
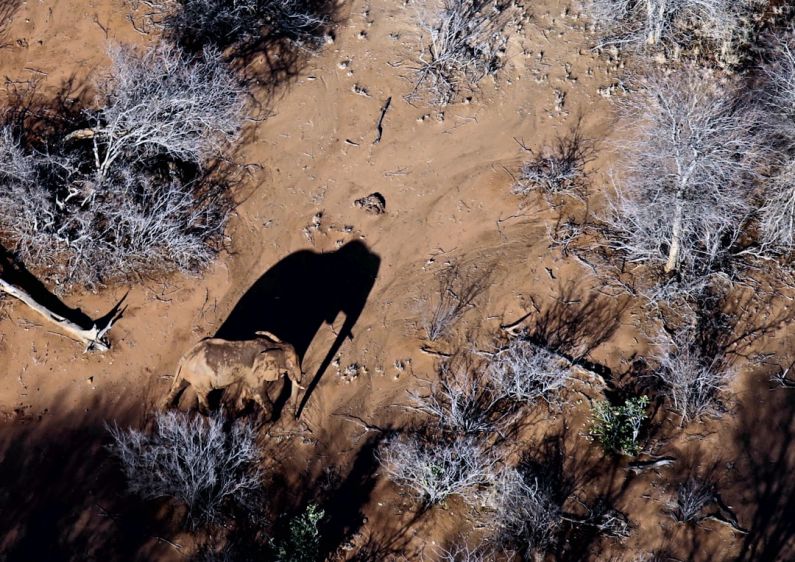
One of the key applications of AI in wildlife conservation is in monitoring and surveillance. Traditional methods of tracking and monitoring wildlife populations can be time-consuming, expensive, and often invasive. AI-powered tools such as drones, camera traps, and satellite imagery have revolutionized the way researchers collect data on wildlife. These technologies can cover large areas quickly and efficiently, providing valuable insights into animal behavior, population dynamics, and habitat use.
AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data collected from these sources, helping researchers identify patterns, trends, and potential threats to wildlife populations. For example, AI can be used to detect poaching activities in real-time by analyzing patterns of movement and identifying suspicious behavior. This enables conservationists to respond quickly and effectively to protect endangered species from illegal activities.
Habitat Conservation and Restoration
Another important application of AI in wildlife conservation is in habitat conservation and restoration. AI algorithms can analyze satellite imagery and other geospatial data to map out habitats, identify areas of deforestation or degradation, and prioritize conservation efforts. By pinpointing areas that are most at risk, conservationists can target their resources more effectively to protect and restore crucial habitats for wildlife.
AI can also be used to optimize conservation strategies, such as habitat restoration projects. By simulating different scenarios and predicting the outcomes of conservation interventions, AI can help researchers make informed decisions about the best course of action to take. This can lead to more successful conservation efforts and better outcomes for wildlife and ecosystems.
Enhancing Anti-Poaching Efforts
Poaching remains a major threat to many endangered species, driven by the demand for wildlife products such as ivory, rhino horn, and exotic pets. AI technology is being increasingly used to combat poaching by improving anti-poaching efforts. For example, AI-powered drones equipped with thermal cameras can patrol protected areas and detect poachers even in low-light conditions. These drones can cover large areas quickly and provide real-time information to law enforcement agencies, enabling them to respond rapidly to poaching incidents.
AI algorithms can also analyze data from camera traps and acoustic sensors to detect signs of poaching activity, such as gunshots or the sound of engines. By alerting rangers to potential threats in real-time, AI technology can help prevent poaching and protect vulnerable wildlife populations.
A Brighter Future for Wildlife Conservation
As the threats to wildlife and ecosystems continue to grow, the role of AI in wildlife conservation is becoming increasingly important. By harnessing the power of AI technology, conservationists can gather and analyze data more efficiently, target their efforts more effectively, and respond to threats more quickly. AI offers new hope for protecting and preserving our planet’s biodiversity, providing innovative solutions to the complex challenges facing wildlife conservation today.
In conclusion, the integration of AI in wildlife conservation represents a new frontier in the fight to protect our planet’s precious biodiversity. By leveraging the capabilities of AI technology, conservationists can work more effectively to safeguard endangered species, restore habitats, and combat illegal activities such as poaching. With AI as a powerful ally, there is hope for a brighter future for wildlife conservation and a sustainable coexistence between humans and the natural world.